In today’s digital age, software development is no longer a solitary endeavor. Developers work in teams across geographies, contribute to global open-source projects, and collaborate with designers, testers, and DevOps engineers. This dynamic environment demands a robust way to track changes, manage collaboration, and ensure that software evolves without chaos. That’s where version control comes in. Read on to find out What Is Version Control and Why Every CS Grad Should Know Git,
For computer science (CS) graduates stepping into the real world of tech, learning version control—especially Git—is non-negotiable. It’s a foundational skill that employers expect and an essential tool for surviving and thriving in modern software ecosystems.
In this blog, we’ll explore what version control is, the different types, why Git stands out, and how mastering Git gives CS grads a serious edge in the job market. We’ll also include tools, real-life examples, and learning resources to help you get started.
What Is Version Control?
Version control is a system for managing changes to code or files over time. It allows multiple contributors to edit, update, and collaborate on code without overwriting each other’s work. It also tracks every change made—who made it, when, and why.
Think of version control as the “track changes” feature in Microsoft Word, but far more powerful and tailored for coding projects.
The Three Types of Version Control
1.Local Version Control Systems (LVCS):
These store versions on a local computer. Tools like RCS (Revision Control System) are early examples. The downside? It lacks team collaboration capabilities.
2.Centralized Version Control Systems (CVCS):
A single central server stores the codebase. Developers pull the latest code, make changes, and push updates. Examples: CVS, Subversion (SVN), and Perforce. While better for teams, CVCS fails if the central server crashes or gets corrupted.
3. Distributed Version Control Systems (DVCS):
DVCS like Git and Mercurial give every contributor a full copy of the codebase, including its history. This allows offline work, better backups, and faster operations.
Why Version Control Is Essential for Developers
Version control isn’t just a luxury; it’s a necessity. Here’s why:
- Seamless Collaboration
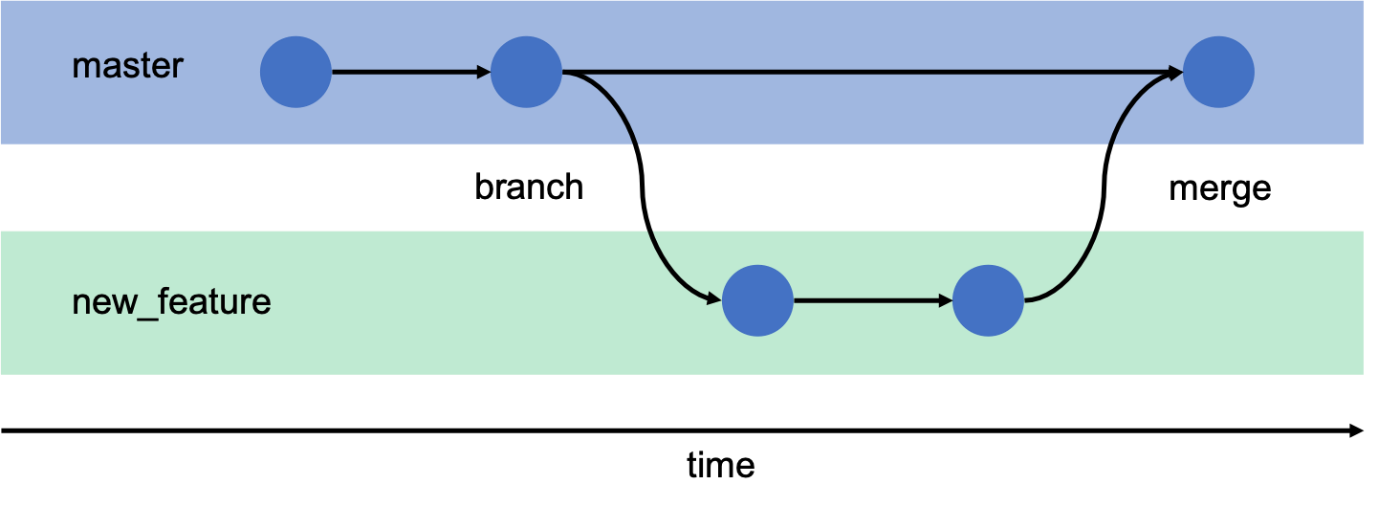
Imagine five developers working on the same file simultaneously. Without version control, managing that code would lead to overwriting, loss of changes, and confusion. With tools like Git, developers can create branches, work independently, and later merge changes, resolving any conflicts along the way.
According to GitLab’s 2023 Global DevSecOps Survey, 77% of organizations say version control improves collaboration and transparency across teams.
- Track and Roll Back Changes
Accidentally broke the code? Want to revert to a previous version? With Git, it takes just one command (git checkout or git revert) to go back to a working state. Every version of your code is saved, allowing you to restore, review, or compare at any point.
- Accountability and History
Every change is documented with a timestamp, message, and author. This is critical for understanding why certain decisions were made, tracking bugs, or managing blame when something breaks.
- Improved Testing and Code Quality
Version control enables continuous integration and automated testing. With Git-based pipelines, every code commit can trigger tests, catch bugs early, and prevent flawed code from reaching production.
Why Git Dominates the Version Control World
Git, created by Linus Torvalds (the creator of Linux) in 2005, has become the global standard for version control.
Git by the Numbers:
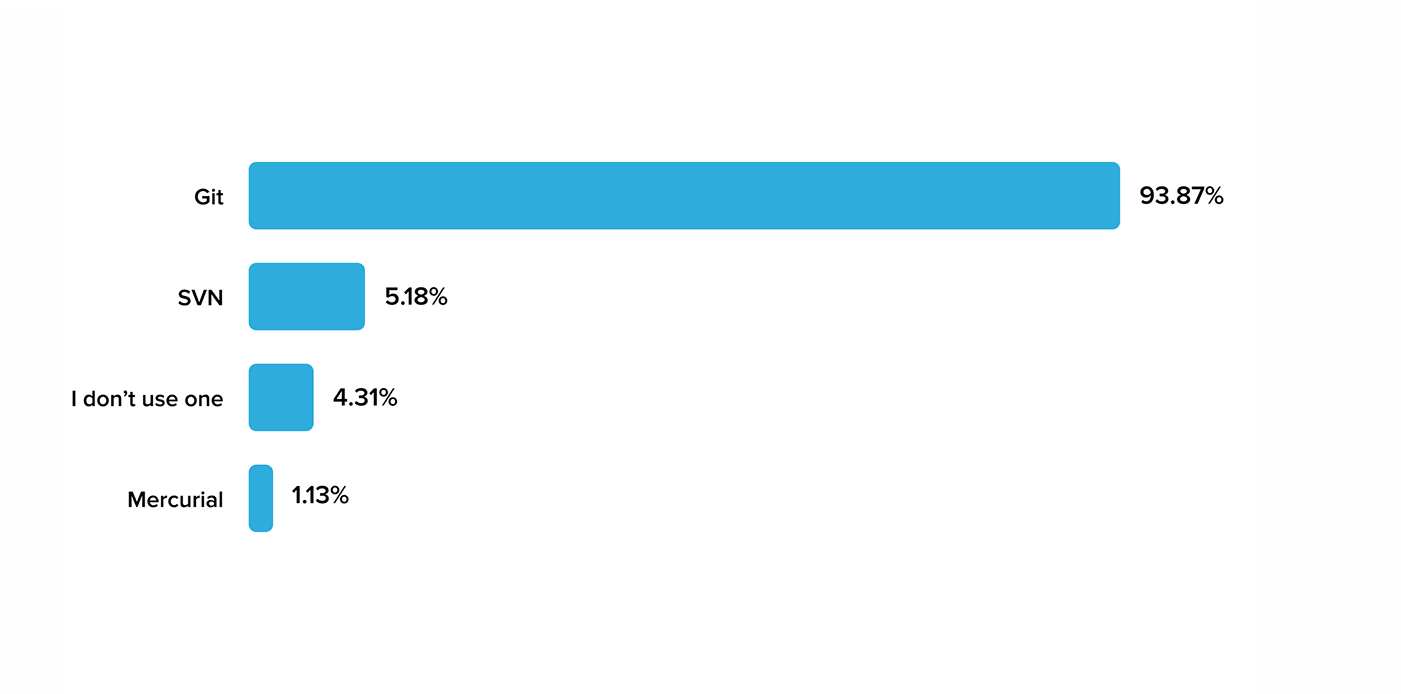
- 93% of developers use Git, according to the 2023 Stack Overflow Developer Survey.
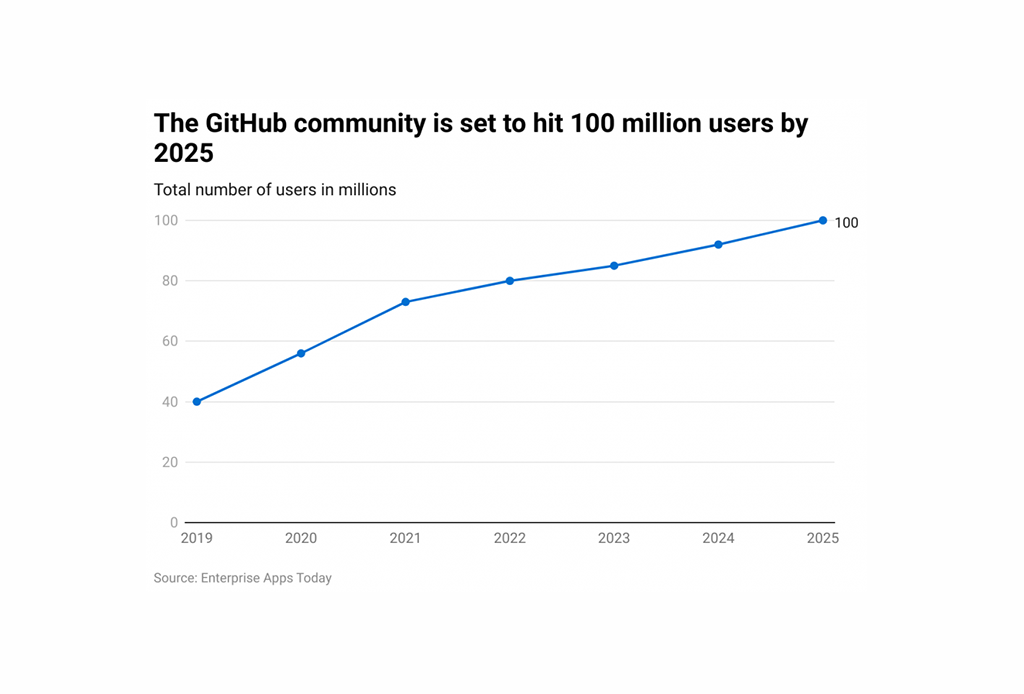
- Over 330 million repositories are hosted on GitHub as of 2024.
- 87% of tech recruiters look for Git knowledge in junior developer resumes (HackerRank Developer Skills Report 2023).
Key Git Features
- Distributed Development: Every user has a full local copy of the codebase. No dependency on a central server.
- Branching & Merging: Create isolated development branches and merge them later—ideal for teamwork and experimentation.
- Speed & Performance: Git is optimized for performance. Operations like commits, diffs, and merges are extremely fast.
- Security: Git uses SHA-1 hashing to ensure data integrity and prevent manipulation.
- Offline Workflows: Developers can commit and view logs even without internet access.
Why Every CS Grad Should Learn Git
- Git Is the Industry Standard
From startups to Fortune 500 companies, Git is the default version control system. Familiarity with Git is assumed for most entry-level roles. In fact, many hiring managers will reject candidates who don’t list Git on their resumes.
- Boosts Collaboration and Communication Skills
Software is rarely built in isolation. Git is tightly integrated with platforms like GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket, which support collaborative development via pull requests, code reviews, issue tracking, and discussions.
Example: If you’re contributing to an open-source project like TensorFlow, React, or Django, you’ll use Git for everything—from cloning the repo to submitting bug fixes.
- Essential for DevOps and Automation
Git isn’t just for coders. It’s at the core of modern DevOps. Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) tools like Jenkins, Travis CI, and GitHub Actions all rely on Git repositories to trigger pipelines.
According to Gartner’s 2023 DevOps Trends Report, companies using Git-based pipelines reported 40% faster feature delivery compared to legacy systems.
- Improves Project and Time Management
With Git, CS grads can manage coursework, internships, and freelance projects more effectively. It offers a structured way to save progress, review previous work, and stay organized.
Real-World Applications of Git
Startups: Git allows agile development and faster iteration. Feature branching makes it easy to prototype ideas without touching the production code.
Enterprises: Large codebases are broken into microservices. Teams often handle hundreds of Git repositories. Companies like Netflix, Facebook, and Shopify manage everything from deployment to rollbacks using Git-based pipelines.
Research and Academia: Professors and students use Git to collaborate on research, track changes to papers, and version-control datasets and Jupyter Notebooks.
Git is now integrated with tools like JupyterLab Git, allowing seamless notebook versioning.
Most Common Git Workflows
Knowing Git isn’t just about memorizing commands. Understanding workflows is essential for real-world projects.
- Feature Branch Workflow
- Create a new branch for each feature (git checkout -b feature-login)
- Merge into main after testing
- Keeps code clean and modular
- Gitflow Workflow
- Uses branches like develop, release, and hotfix
- Suitable for large teams with structured release cycles
- Fork-and-Pull Workflow
- Common in open-source projects
- Developers fork the repo, push changes to their copy, and submit pull requests to the original project
- Trunk-Based Development
- All developers commit to the main branch frequently
- Popular in CI/CD environments for rapid delivery
How Git Improves Your Resume and Hiring Potential
Having Git on your resume isn’t a “nice-to-have”—it’s expected.
- Demonstrates real-world readiness
- Shows ability to work in teams
- Signals contribution to open source
- Helps pass coding interviews that involve Git scenarios
Tip: Maintain a clean and active GitHub profile showcasing your projects, contributions, and commits. Recruiters often browse GitHub to assess candidate quality.
Getting Started with Git
Here’s a roadmap to follow:
- Installation and Setup:
-
- Download and install Git on your local machine (Windows, macOS, or Linux).
-
- Create a GitHub account.
-
- Configure Git with your username and email address using git config.
- Local Repository Management:
-
- Initialize a new Git repository in a project directory using git init.
-
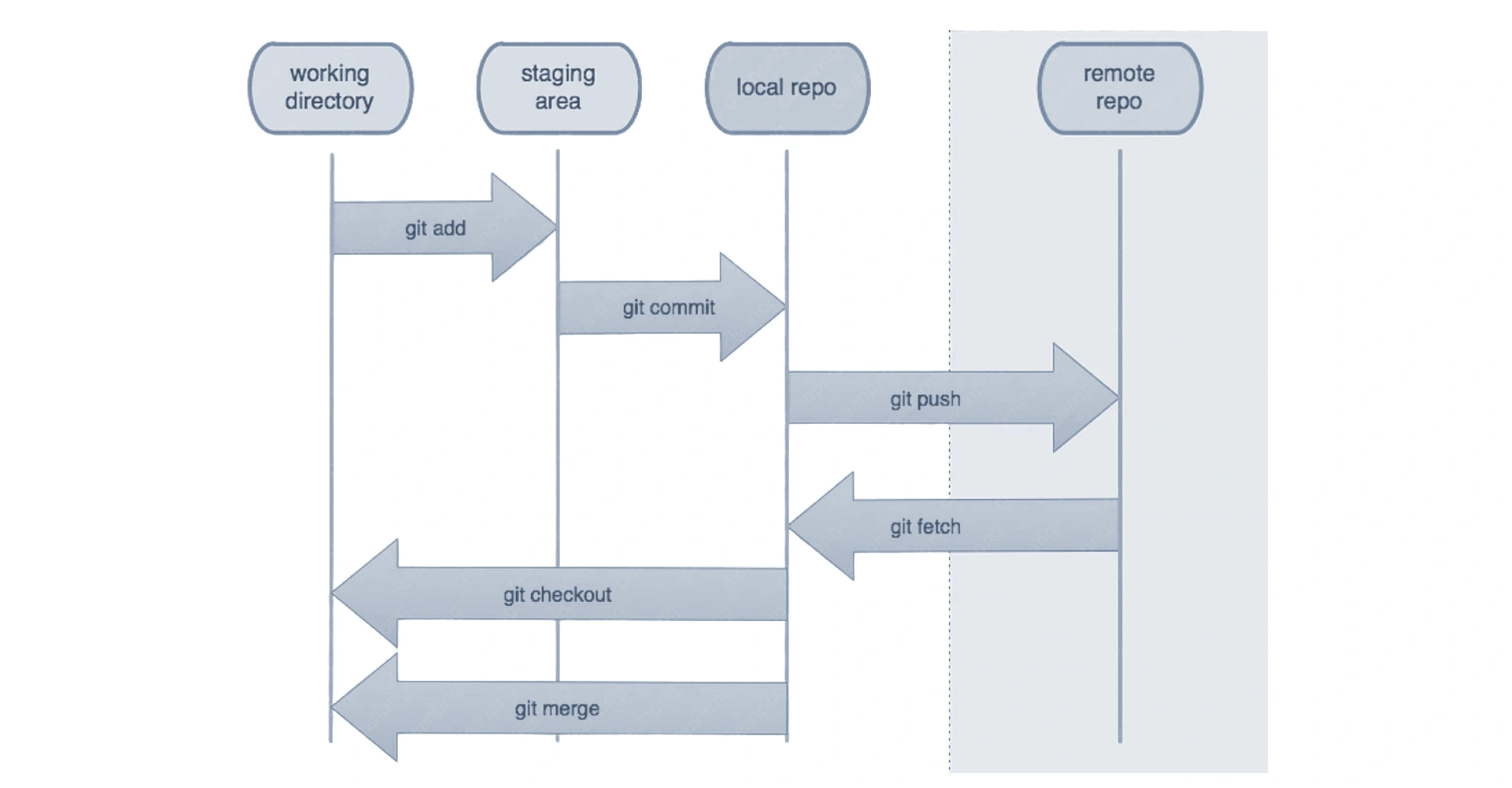
- Understand the Git workflow: Working Directory, Staging Area (Index), and Local Repository.
-
- Add files to the staging area using git add.
-
- Commit changes to the local repository with descriptive messages using git commit.
-
- Check the status of your repository using git status.
-
- View commit history using git log.
- Branching and Merging:
- Create new branches for features or bug fixes using git branch <branch-name>.
- Switch between branches using git checkout <branch-name>.
- Merge changes from one branch into another using git merge.
- Learn to resolve merge conflicts if they occur.
- Remote Repository Interaction (GitHub):
-
- Create a new repository on GitHub.
-
- Link your local repository to a remote GitHub repository using git remote add origin <remote-URL>.
-
- Push local commits to the remote repository using git push.
-
- Pull changes from the remote repository to your local machine using git pull.
-
- Understand git fetch and its difference from git pull.
- Collaboration and Advanced Concepts:
-
- Clone existing repositories from GitHub using git clone.
-
- Fork repositories to contribute to open-source projects.
-
- Create and manage Pull Requests (PRs) on GitHub to propose changes.
-
- Explore concepts like rebasing and stashing for more advanced workflow management.
- Understand tagging for releases.
Tools That Use or Integrate with Git
Git integrates with virtually every modern dev tool:
| Tool | Purpose |
| GitHub | Code hosting, issue tracking, pull requests |
| GitLab | DevOps platform with Git at its core |
| Bitbucket | Git with Jira integration (great for Agile teams) |
| VS Code | Built-in Git support for commits, diffs, etc. |
| Jira | Git integration for tracking code tied to tickets |
| Unity | Supports Git for collaborative game development |
| AWS CodeCommit | Managed Git repos hosted on AWS |
Pro Tips for Mastering Git
- Don’t just learn git commit and git push. Understand concepts like rebase, stash, cherry-pick, and submodules.
- Make mistakes intentionally. Learn to fix merge conflicts, revert commits, and resolve issues.
- Use aliases to simplify long commands.
- Always write clear and informative commit messages (git commit -m “Fix login bug in Auth.js”).
- Practice working on real projects or contributing to open-source.
Final Thoughts
Version control, and Git in particular, is one of the most vital tools in a developer’s toolbox. For computer science graduates, learning Git isn’t optional—it’s expected by employers and required by the realities of modern development. Whether you’re writing code solo, working on team projects, contributing to open-source, or preparing for DevOps roles, Git is the backbone.
Learning Git early sets CS grads apart from the competition and prepares them for real-world engineering challenges. It improves your code quality, strengthens team collaboration, and adds a key credential to your resume.
So don’t wait—install Git, start a repository, and begin tracking your code today.
Since 2010, SynergisticIT has helped 1000’s of job seekers thrive in the tech industry. At SynergisticIT, we make candidates work on technologies and skills our clients demand.
Our unique approach goes beyond training, offering hands-on project experience. We also have a marketing team to promote your skills, so you don’t have to. Check out our candidate outcomes page to see the success stories.
We also participate in industry events like Oracle Java One and the Gartner Data and Analytics Summit, offering excellent opportunities for brand recognition during your job search. Be sure to watch our event videos for more insights.
👉 Explore success stories
👉 Watch our event videos
👉 Read our jobseeker blogs
Furthermore, we have a vast network of clients with whom we can introduce your resume. Since we have been in business since 2010, our brand name association increases your chances of being considered by potential employers. Please visit our Transform Your Future with SynergisticIT | Candidate Outcomes page to learn how we have helped Tech job seekers and how we can jumpstart your tech career!